Quttinirpaaq National Park
Conservation Objectives
To protect threatened species and species of concern, include Porsild’s bryum (a moss), polar bears, and Peary caribou.
Prohibitions
Fishing is prohibited throughout the park, except for Inuit exercising harvesting rights. Access to Fort Conger requires the presence of Parks Canada staff. Visitors must not touch, feed, or entice wildlife, or approach them for photos. Certain areas of the park have restricted or prohibited access, with no camping allowed. Motorized use is generally not allowed in certain areas.
Why (environmental context for protection)
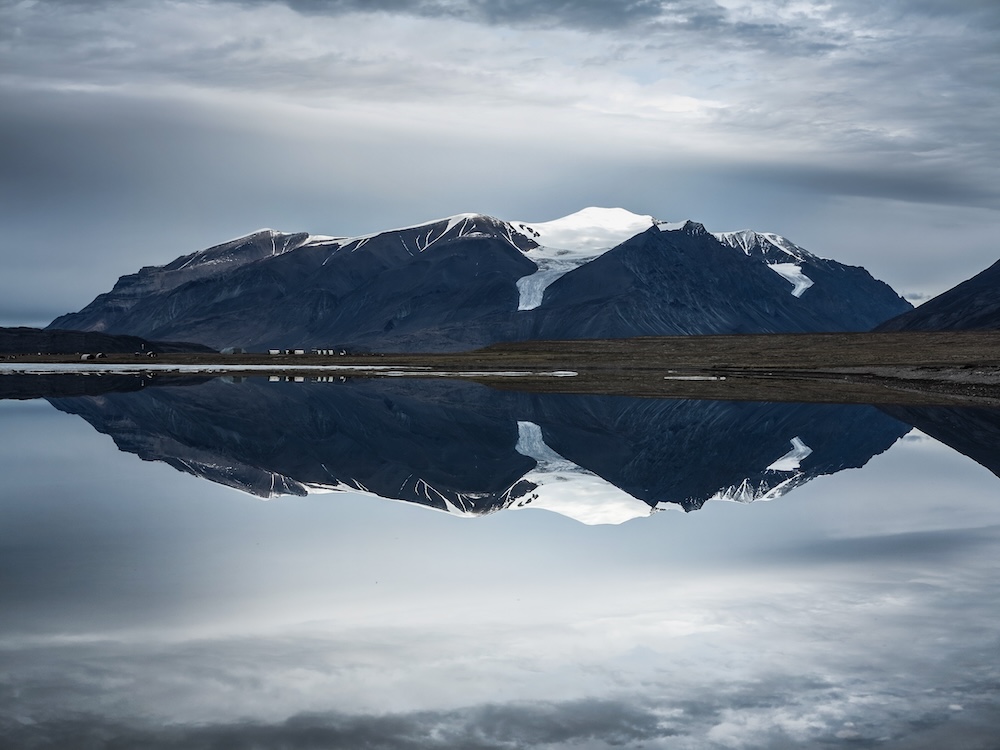
Established in 1988 on Ellesmere Island, Quttinirpaaq National Park occupies the northernmost portion of the Canadian High Arctic. The park is remarkable for its extensive glaciers and ice caps, desert-like conditions, and life forms that are uniquely adapted to the extreme polar environment. Quttinirpaaq is the second largest national park in Canada, protecting 37,775 km2 of eastern High Arctic ecosystem.